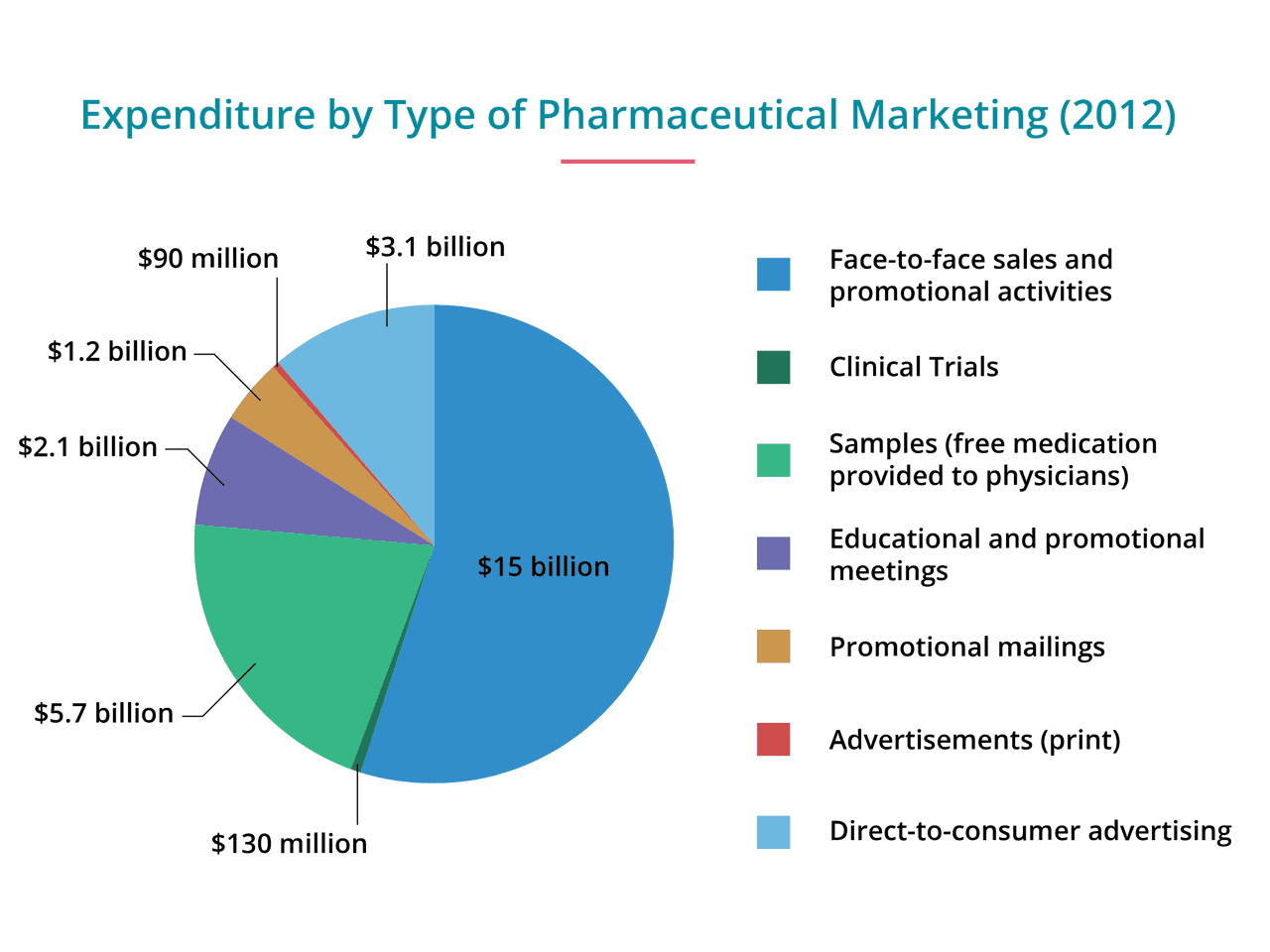
For a patient with severe schizophrenia and a history of poor compliance with oral antipsychotics, the marginal benefit of an injectible over an oral formulation may be extremely high. No government agency is charged with evaluating off-label uses for FDA-approved medications. In fact, Medicaid is the nation’s dominant purchaser of antipsychotic medications, accounting for approximately 80 percent of all antipsychotic prescriptions in The case of antipsychotic medication highlights the impact of products. Psychotropic drugs are playing an increasingly central role in the treatment of mental disorders. Statistics on » Top pharmaceutical drugs «. By , even as the rate of episodes of mental health care had increased, psychotropic drugs were prescribed in about 77 percent of such visits Frank and Glied
High price for low demand
Jannine Poletti-Hughes does not work for, consult, own shares in or receive funding from any company or organisation that would benefit from this article, and has disclosed no relevant affiliations beyond their academic appointment. Blockbuster drugs xrugs been dependent on a high volume of prescription sales. So why the change? Concerns that rare conditions were being neglected by drug developers led to the Orphan Drug Act in the US, the orphan medicinal products regulation by the European Parliament, and other such laws internationally. The incentives on offer include seven years of market exclusivity in the US, and ten years in Europe which may be further extended for paediatric use ; reduced or waived regulatory fees and tax credits.
About the Authors
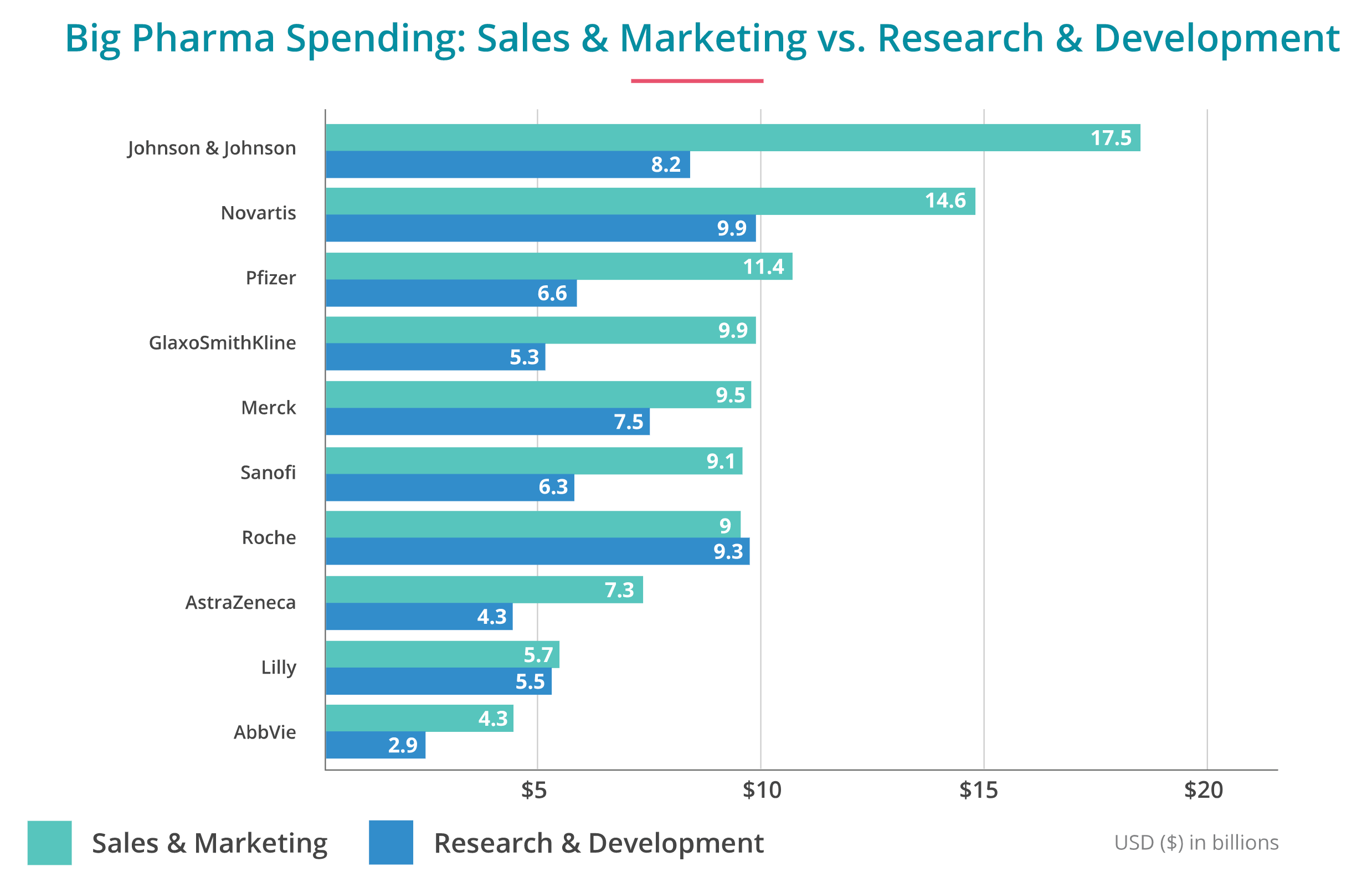
Revenue generated from drug production in the United States has more than doubled in the past ten years. In alone, the U. The major key to this high revenue is repetitive price increases. Drug companies have an unusual ability to function relatively unregulated and to raise drug prices beyond inflation rates. This allows the drug companies to increase their revenues continually, even if the demand for one or more drugs is not high. The result is a huge outpacing of demand in the U. There has been a great deal of focus on new drugs that have been released with sky-high prices.
Me-Too Drugs and Product Reformulations
Jannine Poletti-Hughes does not work for, consult, own shares in or receive funding from any company or organisation that would benefit from this article, and has disclosed no relevant affiliations beyond their academic appointment. Blockbuster drugs have been dependent on a high volume of prescription sales. So why the change? Concerns that rare conditions were being neglected by drug developers led to the Orphan Drug Act in the US, the orphan medicinal products regulation by the European Parliament, and other such laws internationally.
The incentives on offer include seven years of market exclusivity in the US, and ten years in Europe which may be further extended for paediatric use ; reduced or waived regulatory fees and tax credits. These have been very successful so far: the Food and Drug Administration has approved more than drugs for rare diseases since the US law came into force, compared with fewer than ten such products in the decade before. Niche drugs can command hefty prices.
Although these are prescribed to fewer patients, their high prices can how much money do pharmaceutical companies make from psycotropic drugs in revenues equivalent to traditional blockbusters. The pharmaceutical industry is acutely aware of. Our recent analysis of the companies which market nearly orphan drugs provides even more damning evidence. This suggests that policies directed towards incentivising orphan drug development have worked to the extent that companies are profiting excessively.
So what can be done? Orphan drug status could be redefined, incentives might be reduced and prices could be controlled. The pharmaceutical industry will likely oppose such measures. While orphan drugs are for rare diseases that are serious or potentially life threatening, a distinction could be made between drugs with specific use for one condition often for ultra-rare hereditary diseasesand those used in a number of conditions.
Gleevec imatinibfor instance, has European Medicines Agency orphan status for seven different cancers. The duration of market exclusivity could also be better linked to the revenue generating potential of each orphan drug. Under the orphan medicinal products regulation in the EU, member states can trigger a review of the profitability of individual products to limit the period of monopoly to six years. This is to allow other companies to enter the market sooner, promote competition and put downward pressure on prices.
Whatever steps are taken, appropriate policies are needed now to stop orphan drugs becoming less affordable for patients in need while companies get more profitable. Between the Sand and the Sea: Oman’s architectural heritage — Liverpool. Lest we forget? Edition: Available editions United Kingdom. Rare diseases have turned into big business. High price for low demand Niche drugs can command hefty prices.
The focus used to be on making money from high sales of commonly used products. Lisa S. Rare diseases Medication Drugs. Most popular on The Conversation Could invisible aliens really exist among us?
Adopting orphans
Rockville, Md. I first discuss whether me-too products and reformulations indeed add little value. This article outlines the policy issues related to psychotropic drugs with respect to their role in determining access to mental health treatment and the cost and quality of mental health care. Second, as the globalization of mental health has unfolded over the past several decades, the burden of mental disorders has increased in tandem. Atypical Antipsychotic Medications. Those institutions that are responsible for managing medical care also have contributed to the expanded use of psychotropic medications. The entry of generic equivalents has consequently altered the market’s price structure. Revenue in in Million U. PBMs create competition among manufacturers within a therapeutic class such as the SSRIs for the placement of their products in the second rather than the third tier. Friedman says the lack of interest in finding the next how much money do pharmaceutical companies make from psycotropic drugs groundbreaking medications is in part due to the difficulty of bringing psychotropic drugs to market. However, evidence from the Medicaid rebate program, which requires manufacturers to pay rebates of Simon G. Pharmaceutical Industry in the U. At the same time Dr Ewen Cameron, the head of psychiatry at McGill, Canada, America, and the World, was leading psychiatry in the destructive direction that Robert Whitaker has described so well, leading to the epidemic of mental illnesses and addictions that we see today, so I fled to Britain for therapy and psychoanalysis. A paid subscription is required for full access. Private third-party payments for antipsychotic and antidepressant drugs added up to 40 percent of spending for pharmaceuticals in Novartis Basic Account.
Comments
Post a Comment